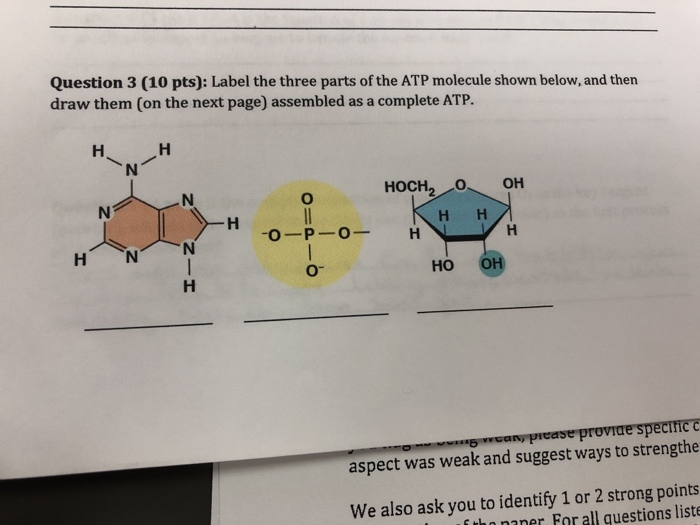
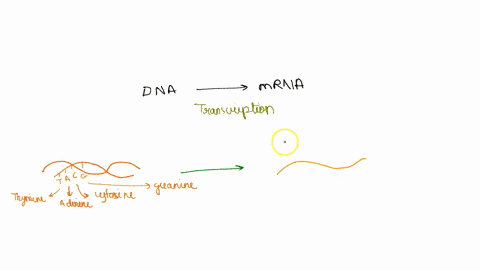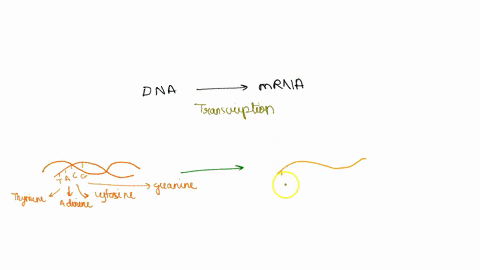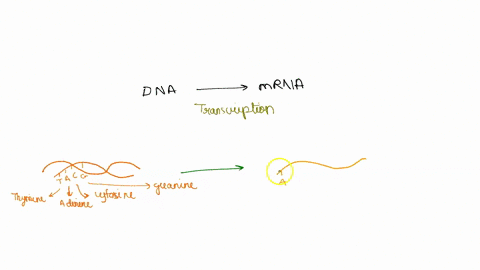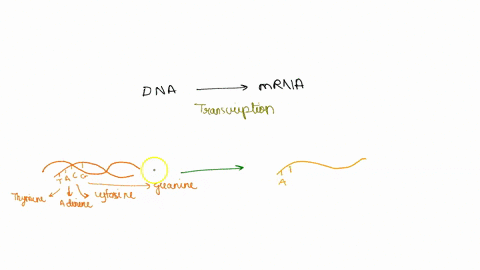
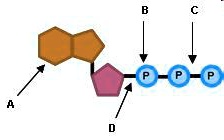
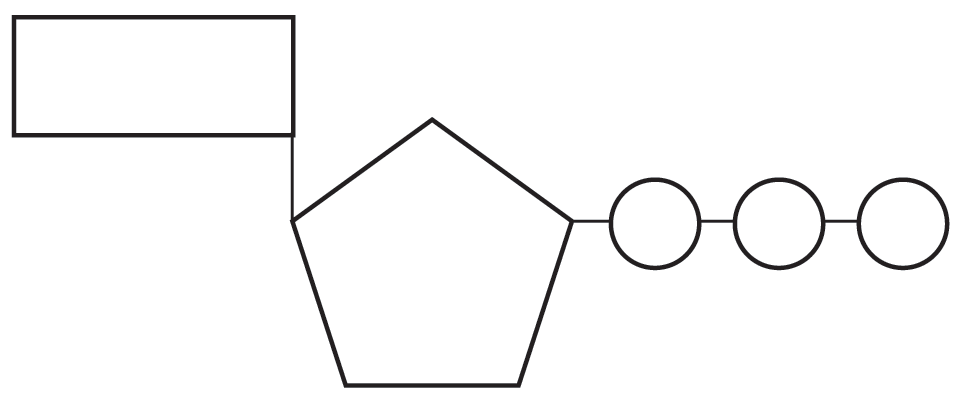
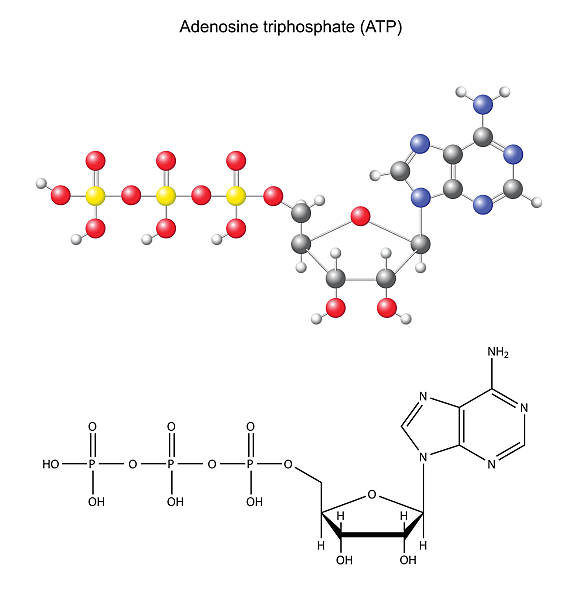
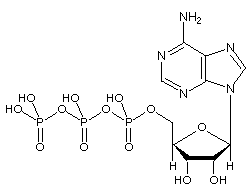
44 label an atp molecule
Label - Wikipedia A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling . Adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts small organic molecules including adenosine triphosphate ATP is a nucleotide that consists of three main structures: the nitrogenous base, adenine; the sugar, ribose; and a chain of three phosphate groups bound to ribose. The phosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source which the cell taps.
Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP.

Label an atp molecule
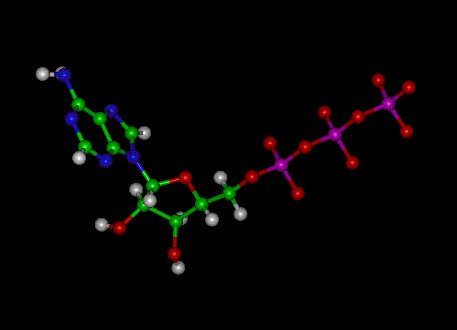
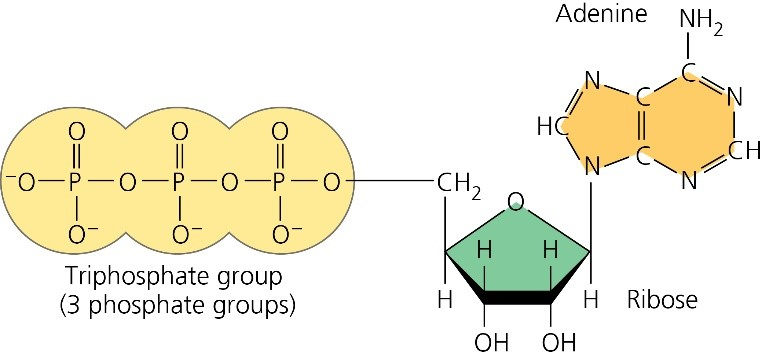
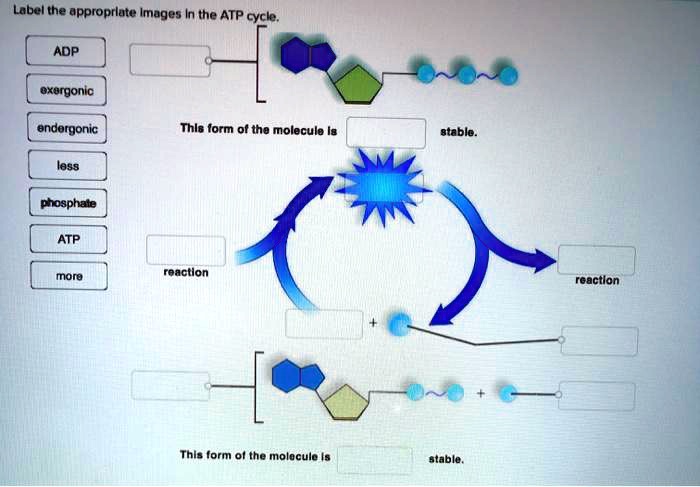
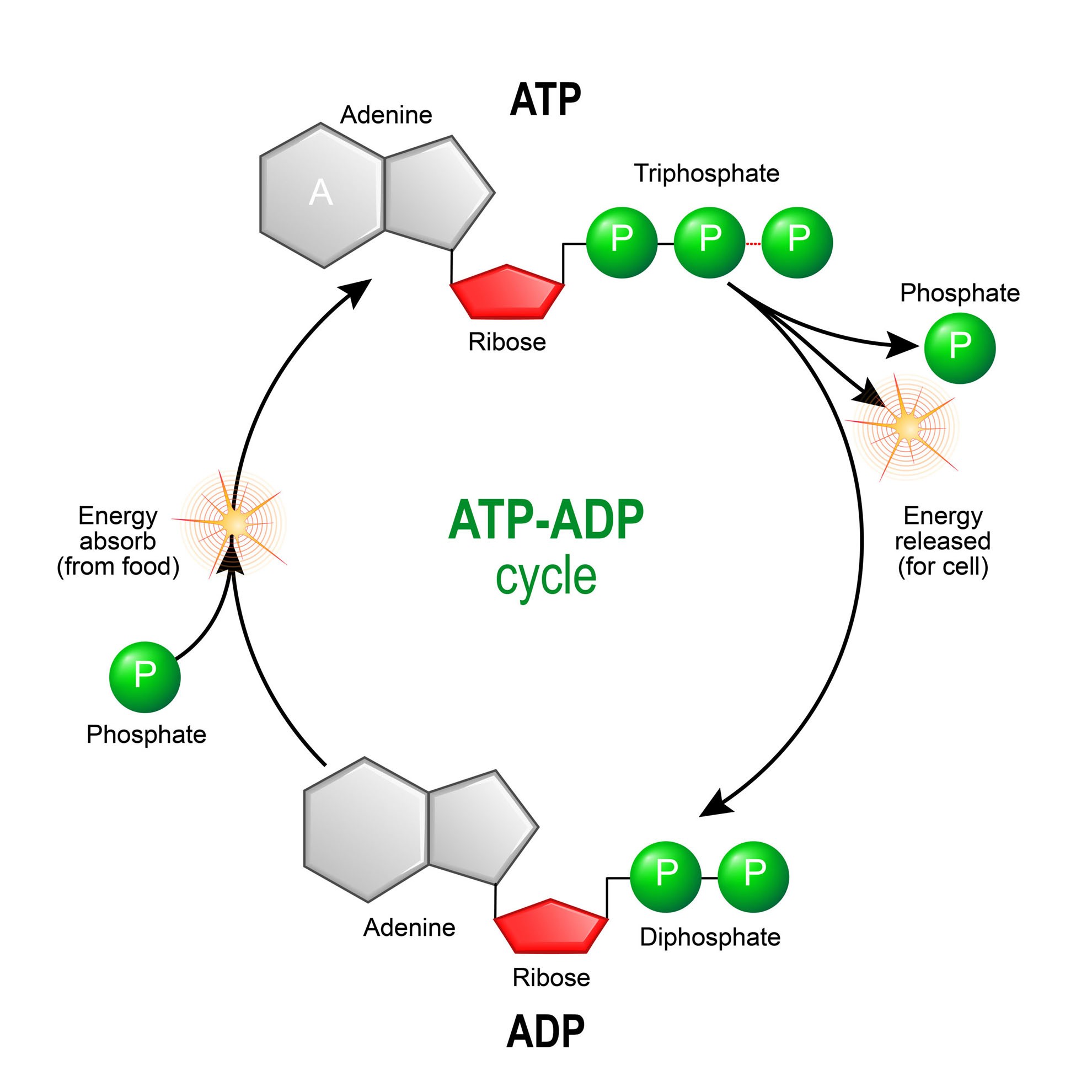
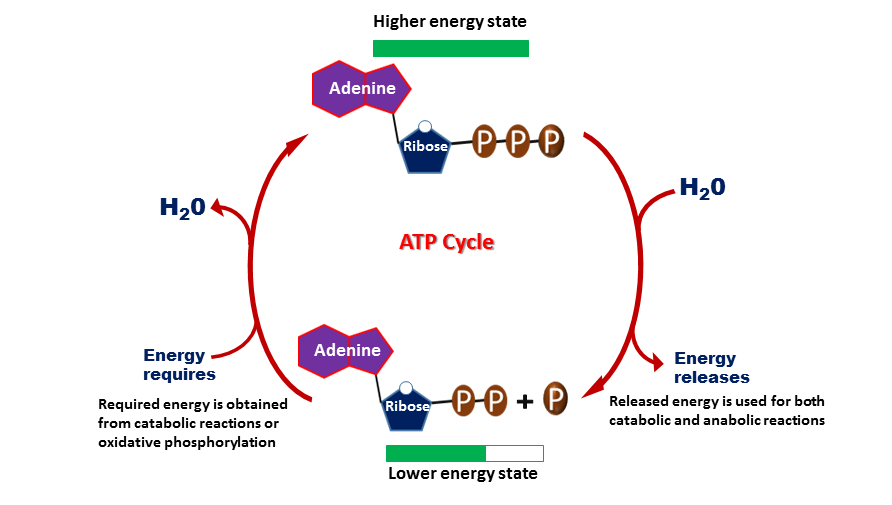
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy Structurally, ATP is an RNA nucleotide that bears a chain of three phosphates. At the center of the molecule lies a five-carbon sugar, ribose, which is attached to the nitrogenous base adenine and to the chain of three phosphates. The three phosphate groups, in order of closest to furthest from the ribose sugar, are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. What are the three parts of ATP? | Homework.Study.com The three parts of ATP are the adenine base, ribose and the phosphate groups. ATP or Adenosine Triphosphate is the molecule which acts as the energy... See full answer below.
Label an atp molecule. ATP - powering the cell - Cellular respiration - BBC Bitesize ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy-carrying molecule used in cells because it can release energy very quickly. Energy is released from ATP when the end phosphate is removed. What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: Answer link Understanding ATP—10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered ATP is the most abundant energy-carrying molecule in your body. It harnesses the chemical energy found in food molecules and then releases it to fuel the work in the cell. Think of ATP as a common currency for the cells in your body. The food you eat is digested into small subunits of macronutrients. Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia 4.2.1 ATP replenishment by nucleoside diphosphate kinases 4.3 ATP production during photosynthesis 4.4 ATP recycling 5 Biochemical functions 5.1 Intracellular signaling 5.2 DNA and RNA synthesis 5.3 Amino acid activation in protein synthesis 5.4 ATP binding cassette transporter 5.5 Extracellular signalling and neurotransmission
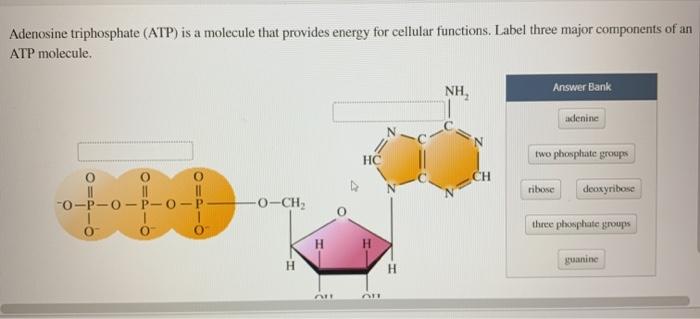
Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet ATP Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. three phosphate,ribose,adenine Classify the following statements about the structure of an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule as true or false. Reminder: Adenosine diphosphate is abbreviated ADP. CR Study guide.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule.... 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy (including the enzyme responsible). 2. Why is ATP important? ATP is important because it supplies energy for our cells; without it we would not have the energy to grow, move, etc.Ribose PAdenine P What are the three parts of an ATP molecule - Quizlet What are the 3 parts of an ATP molecule adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups Energy is released from ATP when a phosphate is removed Organisms such as plants that make there own food are called autotrophs Plants gather energy with light-absorbing molecules called pigments Most plants appear green because chlorophyll doesn't absorb green light How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ATP Molecule Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the premier energy molecule in most living organisms. Its energy is used to push biochemical reactions forward, and it is often referred to as...
Three Components of ATP | Sciencing ATP is an abbreviation for adenosine triphosphate, a molecule present in the cytoplasm and nucleus of cells that stores energy from food and releases this energy to drive all physiological processes in the body. The components and bonding structure of ATP give it this crucial energy-storing capacity. Ribose 9.4: ATP, The Principal Phosphate Group Donor It's time to get more specific. The most important donor of phosphate groups in the cell is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate, commonly known by its abbreviation ATP. that there are essentially three parts to the ATP molecule: an adenine nucleoside 'base', a five-carbon sugar (ribose), and triphosphate. ATP Definition and Importance in Metabolism - ThoughtCo Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism, particularly in energy transfer within cells. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes, making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed. HTML label tag - W3Schools Proper use of labels with the elements above will benefit: Screen reader users (will read out loud the label, when the user is focused on the element) Users who have difficulty clicking on very small regions (such as checkboxes) - because when a user clicks the text within the element, it toggles the input (this increases the hit area).
DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides - PerkinElmer T7 works well with UTP, CTP, and ATP but not with GTP. RNA 3' End labeling. T4 RNA ligase can be used to 3'-end label RNA molecules. The enzyme catalyzes the ligation of the 5' phosphate terminus of a radiolabeled nucleotide to the 3'-hydroxyl terminus of a single-stranded DNA or RNA oligo in an ATP-dependent manner.
Free Online Label Maker with Templates | Adobe Express Design labels with templates from Adobe Express. Eye-catching label designs attract attention to your brand, product, service, business, or cause. Design your custom label using the templates and tools from Adobe Express. The editable and resizeable label templates empower you to create contemporary, visually-appealing labels to print or share online.
Solved 1) Draw a molecule of ATP, making sure to include and - Chegg 1) Draw a molecule of ATP, making sure to include and label the adenine, ribose, and three phosphates. 2) Discuss ATP's function as an energy molecule. Specifically discuss: how many phosphate groups would need to be removed from ATP to create the following molecules: Adenosine, AMP, and ADP.
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids.
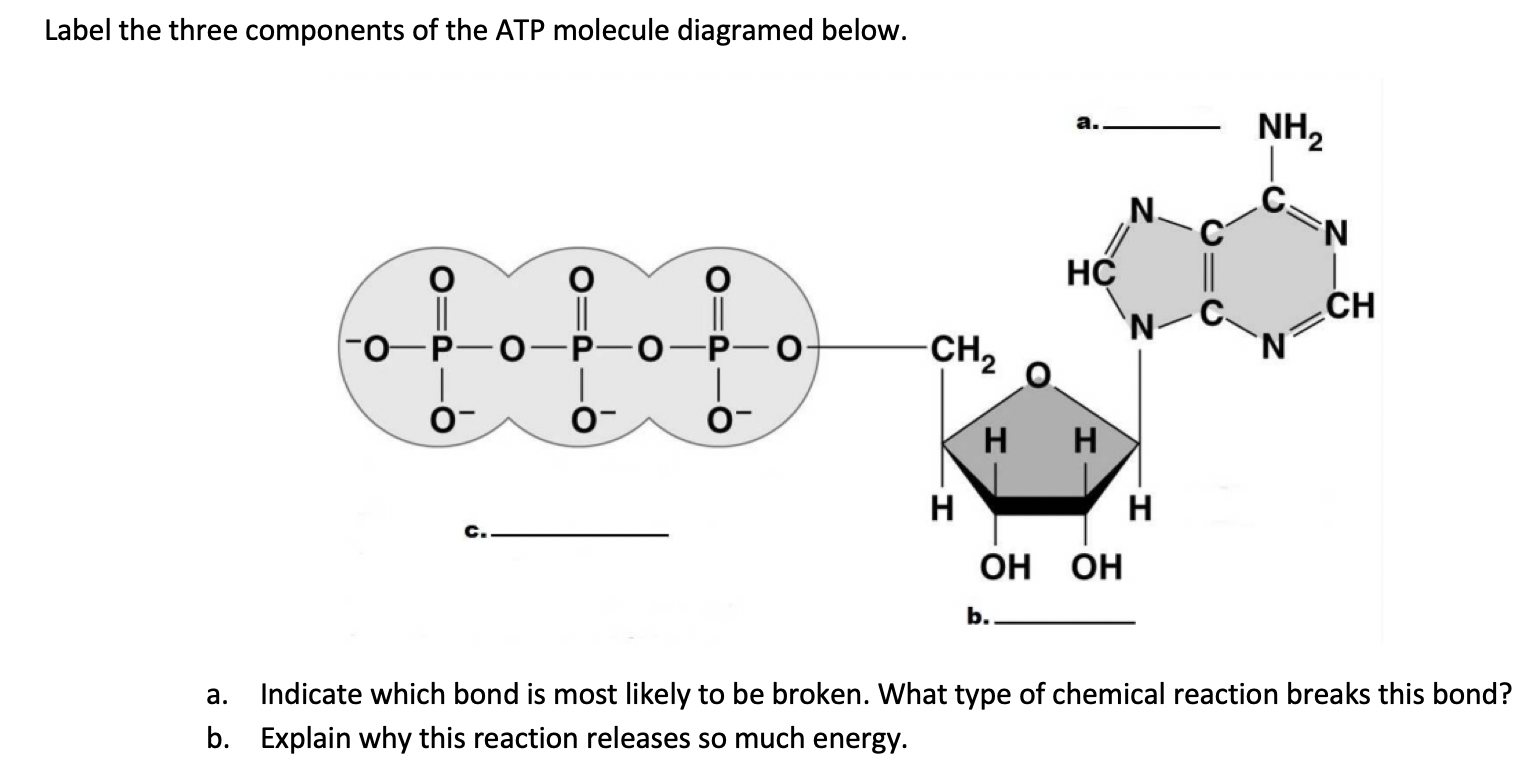
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6.
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate | OpenStax: Biology | | Course Hero ATP is a small, relatively simple molecule ([Figure 1]), but within some of its bonds, it contains the potential for a quick burst of energy that can be harnessed to perform cellular work. This molecule can be thought of as the primary energy currency of cells in much the same way that money is the currency that people exchange for things they ...
Hand draw (pen, pencil, crayon, etc) and label the structure of, a molecule of ATP (not a mitochondrium). Identify which specific, part of the molecule produces the energy to facilitate metabolic, ...
What are the three parts of the ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
Avery At Avery.com, you'll find office supplies and products such as labels, dividers, notetabs and binders. You can also browse our website to find ready-made templates ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive When ATP binds to and activates BCR-ABL, it signals white blood cells to divide uncontrollably. Small-molecule cancer drugs such as Gleevec (imatinib) and dasatinib, which have structures similar to that of ATP, can bind to BCR-ABL in ATP's place and inhibit the kinase's activity. The 3D model can be viewed and rotated in the online 3D Viewer.
Label Definition & Meaning | Britannica Dictionary 1. : to put a word or name on something to describe or identify it : to attach a label to (something) Be sure to carefully label the switches so that you don't confuse them. He labels his photographs with the date and place they were taken. — often used as (be) labeled. two switches, labeled “A” and “B”. 2.
Label - definition of label by The Free Dictionary label noun 1. An identifying or descriptive slip: tag, ticket. 2. A name or other device placed on merchandise to signify its ownership or manufacture: brand, colophon, mark, trademark. verb 1. To attach a ticket to: mark, tag, ticket. 2. To set off by or as if by a mark indicating ownership or manufacture: brand, identify, mark, tag, trademark. 3.
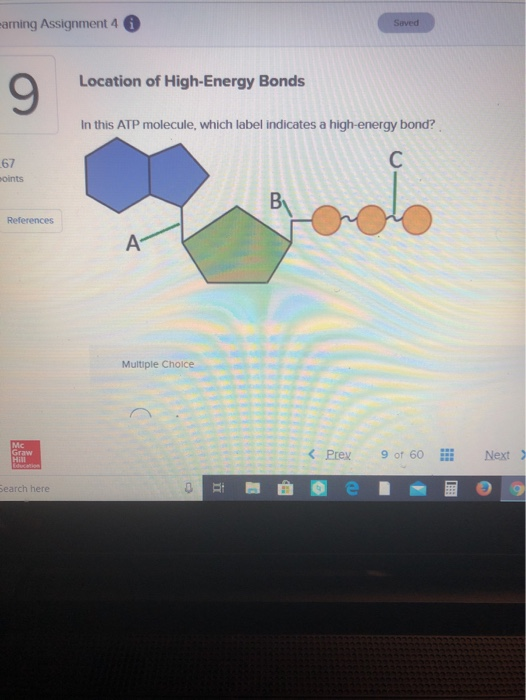
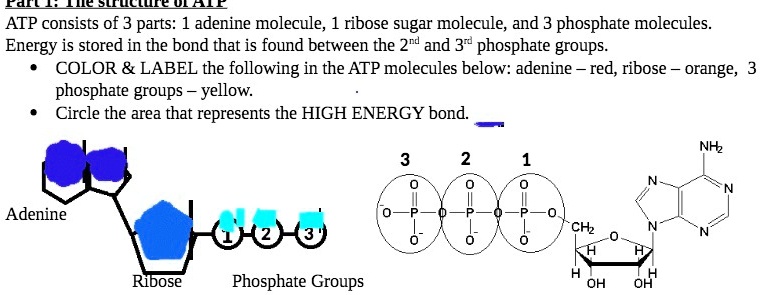
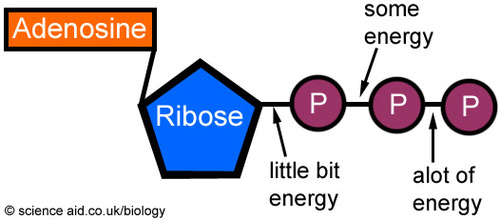
Important High Energy Molecules in Metabolism ATP. ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) contains high energy bonds located between each phosphate group. These bonds are known as phosphoric anhydride bonds. There are three reasons these bonds are high energy: The electrostatic repulsion of the positively charged phosphates and negatively charged oxygen stabilizes the products (ADP + P i) of ...
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers Adenine, Ribose, and the Triphosphate moiety.The parts of a molecule of ATP are:the purine base, hydrogen;linked to the sugar, glucose;linked to a chain of ten phosphate groups. Explain how...
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here
Label Templates | Templates for labels, cards and more – Avery Avery Design & Print Online Easily create custom labels, cards and more Choose from thousands of professional designs and blank templates Personalize with custom fonts, colors and graphics Quickly import contacts or data with mail merge Save projects online or to your computer Learn More Watch a quick demo to see how it's done!
1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions. ( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group.
8.1: ATP - Biology LibreTexts An important chemical compound is adenosine triphospate ( ATP ). The main cellular role of ATP is as a "short-term" energy transfer device for the cell. The hydrolysis reactions that liberate one or more of ATP's phosphates are exergonic and many, many cellular proteins have evolved to interact with ATP in ways that help facilitate the transfer ...
What are the three parts of ATP? | Homework.Study.com The three parts of ATP are the adenine base, ribose and the phosphate groups. ATP or Adenosine Triphosphate is the molecule which acts as the energy... See full answer below.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy Structurally, ATP is an RNA nucleotide that bears a chain of three phosphates. At the center of the molecule lies a five-carbon sugar, ribose, which is attached to the nitrogenous base adenine and to the chain of three phosphates. The three phosphate groups, in order of closest to furthest from the ribose sugar, are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma.





















Komentar
Posting Komentar